Welcome to the new era of work—one where the rigid 9-to-5 is giving way to agile, flexible arrangements that empower both businesses and professionals.
As companies strive to remain competitive and innovative, fractional employment has emerged as a strategic solution. Fractional contracts enable organizations to access specialized talent without the overhead of traditional full-time roles. In addition, they offer individuals the opportunity to diversify their skills and enhance their work-life balance.
Fractional contracts formalize these modern work arrangements, detailing everything from work scope and compensation models to contract duration and termination clauses. In this guide, we’ll be exploring the key components of fractional contracts and their benefits for employers and employees alike. We’ll also consider the challenges that may arise when implemented.
Whether you’re a business leader eager to streamline operations or a professional looking to reclaim control over your schedule, fractional contracts offer a clear pathway to innovation, efficiency, and professional fulfillment.
Understanding Fractional Employment
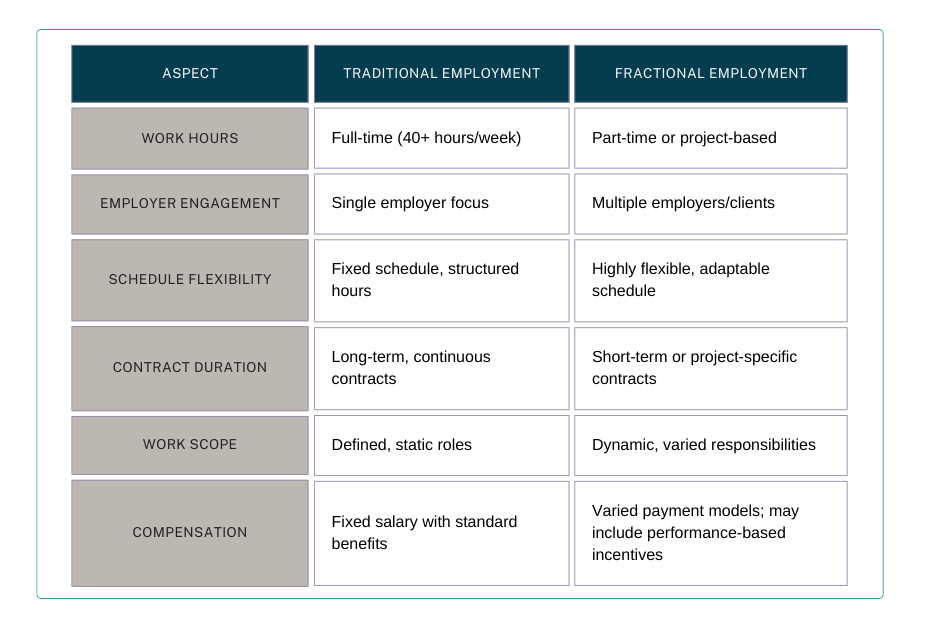
Fractional employment offers a flexible and dynamic approach to work that breaks away from the traditional employer/employee model.
At its core, fractional employment allows individuals to divide their expertise and work hours across multiple employers or projects, enabling them to contribute to various organizations simultaneously.
This arrangement is often part-time but can offer a higher degree of flexibility compared to standard part-time roles. Unlike full-time employment, which traditionally binds employees to one organization, fractional employment prioritizes adaptability—both for the individual professional and the business.
As a result, both employers and employees can tap into a broad spectrum of benefits. For employers, fractional workers bring specialized skills to the table without the long-term commitment or significant overhead costs of full-time hires.
Employees, on the other hand, find rich opportunities to diversify their portfolios, work on intriguing projects across different sectors, and manage their work-life balance with greater ease.
The scope of fractional employment often varies depending on the contract. Typically, fractional workers may focus on a specific area of expertise, such as marketing, finance, or tech development. However, this can differ from one arrangement to the next based on the needs of the business.
In essence, fractional contracts offer a highly customized and versatile framework that can be shaped to meet the demands of both organizations and workers. It’s this very flexibility that makes fractional employment attractive in today’s rapidly changing business environment.
Traditional vs. Fractional Employment
 Anatomy of a Fractional Contract
Anatomy of a Fractional Contract
Fractional contracts are the formal agreements that provide the framework for fractional employment. These contracts differ from traditional full-time agreements in several key ways. They offer greater flexibility while still maintaining important legal and structural protections for both employer and employee.
One of the defining features of a fractional contract is its flexibility in terms of duration. Unlike long-term, fixed contracts in traditional roles, fractional contracts often have shorter terms tailored to specific projects or business needs. This allows employers to scale their workforce quickly while giving workers the autonomy to choose multiple engagements based on their personal schedules and professional goals.
Another integral component of fractional contracts is the compensation model. While full-time employment typically involves a fixed salary and benefits package, fractional work often includes a variety of payment structures, such as:
- Hourly rates
- Fixed project fees
- Or performance-based pay.
Employers can negotiate compensation based on the value of the skills required and the scope of work, while contractors gain more control over their earnings. The work scope in rotational contracts is also generally more dynamic than in traditional contracts.
Given the nature of fractional agreements, tasks and expectations are usually defined project-by-project, allowing businesses to bring in specialized skill sets only when needed. This differentiates fractional work from the more static roles often seen in full-time positions, which may involve purely repetitive tasks in a long-term, unchanging framework.
Lastly, fractional contracts often contain termination, renewal clauses, and specific flexibility provisions. Whether it’s deciding on early contract termination or adjusting the terms to meet shifting needs, these contracts are designed to be more adaptable than traditional employment contracts.
These elements protect both parties by creating clear procedures and expectations while still keeping the arrangement flexible. To navigate these complexities, legal compliance is key. It’s essential that fractional contracts adhere to labor laws, tax regulations, and various stipulations that protect employee rights.
Drafting contracts with these principles in mind ensures a fair, balanced work relationship and minimizes risks for both sides. With these essential elements in place, fractional contracts help facilitate a flexible, results-driven employment model that can adapt to evolving demands, making it an excellent option for today’s professional landscape.
The Benefits of Fractional Contracts
Fractional contracts offer a range of benefits that create a win-win scenario for employers and employees.
For companies, these agreements provide the opportunity to precisely scale talent in line with current project demands, reduce overhead costs, and maintain a competitive edge in rapidly shifting markets.
Meanwhile, professionals gain the freedom to select projects that align with their skills and lifestyle, fostering both professional growth and a healthier work-life balance. The benefits for each party include:
For Employers:
- Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability: Optimize budgets by hiring specialized talent only when needed.
- Access to Specialized Skills: Tap into niche expertise on-demand without the long-term commitment of a full-time hire.
- Enhanced Organizational Agility: Quickly adjust staffing levels to respond to evolving business needs.
For Contractors:
- Improved Work-Life Balance: Enjoy flexible scheduling that accommodates personal commitments.
- Opportunities to Diversify Skills: Engage in a variety of projects that contribute to professional growth.
- Increased Professional Autonomy: Benefit from greater control over workload and career trajectory.
Challenges and Strategies for Success
While fractional contracts offer flexibility and innovation, their implementation comes with several challenges that need to be proactively addressed. Below are some common pitfalls businesses and professionals may encounter, as well as effective strategies to mitigate them:
-
Pitfall: Communication and Coordination Challenges
Fractional workers often collaborate with multiple teams or employers, leading to potential miscommunication or misunderstandings about expectations, timelines, and project scope.
Mitigation Strategy: Establish clear and consistent communication channels—whether via project management tools, regular check-ins, or team collaboration platforms—to ensure alignment.
Additionally, maintain a centralized document or shared workspace for project-related details that can be accessed effortlessly by all stakeholders.
-
Pitfall: Maintaining Productivity and Accountability
With flexible work schedules and multiple work commitments, fractional workers may face difficulty staying consistently productive or meeting deadlines, especially when managing several projects concurrently.
Mitigation Strategy: Implement performance evaluation mechanisms and measurable key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide oversight without compromising autonomy.
Regular evaluations and feedback loops can ensure quality and productivity remain consistent while allowing fractional workers to adjust where needed.
-
Pitfall: Ensuring Fair Compensation and Benefits
The complexity of compensation models and the variable nature of fractional work can lead to confusion about fair pay or lack of benefits typically associated with full-time employment.
Mitigation Strategy: Be transparent about compensation terms upfront. Define whether payment will be hourly, project-based, or performance-driven, and clarify whether any benefits (e.g., health insurance, retirement contributions) will be provided, even at a prorated level, for part-time employees.
-
Pitfall: Managing Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Fractional employment relationships carry legal complexities, from intellectual property rights to tax implications to local labor laws, especially when dealing with remote or cross-border workers.
Mitigation Strategy: Work with legal professionals who specialize in labor law to ensure all formal agreements comply with relevant regulations. Standardize contract templates to include key legal protections such as non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), intellectual property clauses, and clear terms regarding tax responsibilities and local laws.
By addressing these common pitfalls with targeted strategies, businesses can successfully navigate the complexities of fractional contracts, ensuring both efficiency and compliance while fostering positive and productive relationships with their fractional workforce.
Best Practices for Implementing Fractional Contracts
- Set Clear Expectations: Define deliverables, timelines, and performance indicators upfront so that both parties understand their responsibilities.
- Establish Robust Communication Channels: Use reliable digital tools and schedule regular meetings to keep all stakeholders connected.
- Implement Continuous Performance Evaluation: Regularly assess progress with structured feedback loops, allowing for timely adjustments to workload and expectations.
- Maintain Transparent Compensation Structures: Clearly outline payment terms and review them periodically to ensure fairness and alignment with market standards.
- Ensure Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Involve legal experts to draft contracts that are fully compliant with relevant laws, reducing risk and safeguarding intellectual property.
- Foster a Collaborative Culture: Encourage open dialogue, inclusivity, and teamwork to build trust and maintain high morale across fractional teams.
By proactively addressing potential pitfalls with these targeted strategies and best practices, organizations can mitigate risks and fully harness the flexibility and value that fractional contracts offer.
The Future of Work and Fractional Employment
Fractional contracts represent a forward-thinking solution that combines flexibility with strategic precision. As the workplace continues to evolve, the future of fractional employment appears increasingly promising—driven by technological innovations and a growing demand for adaptable work arrangements. This model not only empowers organizations to scale efficiently and tap into specialized talent but also enables professionals to enjoy a healthier work-life balance and diversify their expertise.
Looking ahead, we can expect fractional contracts to further reshape traditional work paradigms, encouraging businesses to become more agile and innovative in response to rapidly changing market dynamics. Organizations that embrace these trends will be well-positioned to attract top talent, reduce overhead costs, and maintain a competitive edge in an ever-changing landscape.
Ready to transform your workforce strategy and embrace the future of work? Connect with us today to explore how fractional contracts can drive your organization forward and unlock new opportunities to reach your audacious goals!



