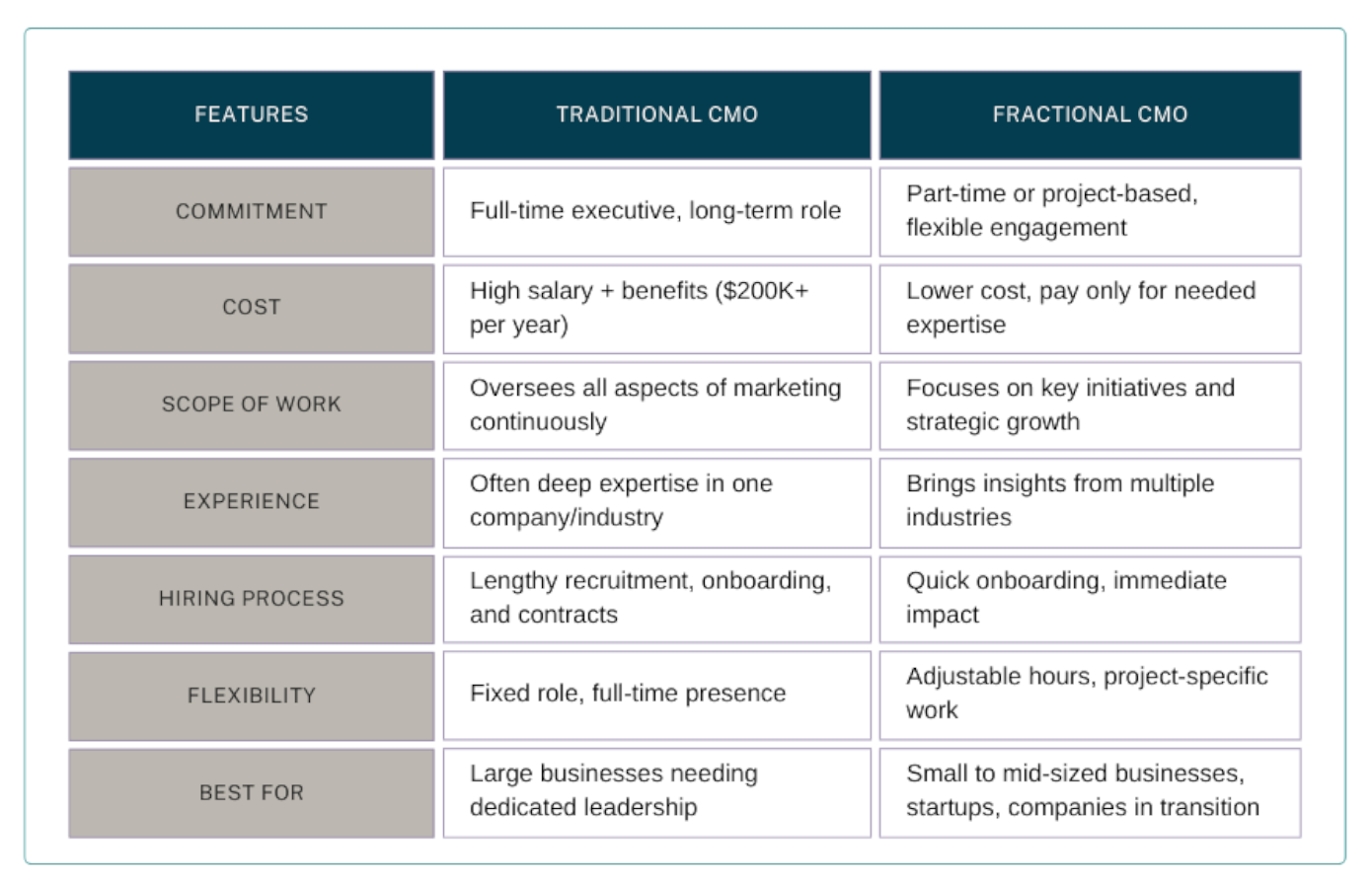
If you think of fractional meaning, what comes to mind? If you’re like most people, your first thought may be “math.” Something divided, partial, or incomplete—a fraction. But in the modern business world, fractional often means something very different, especially when it comes to leadership. It’s not a “fraction” of what you need. It’s getting the exact type of leadership you need, often at a fraction of the cost and hassle.
At its core, fractional is a leadership model in which experienced executives step into a company part-time to provide senior-level support without the cost, commitment, or risk of a full-time hire. It’s a strong solution for companies that need expertise yesterday.
Of course, the real fractional meaning is deeper than a simple definition.
Fractional leadership can be powerfully meaningful. Companies gain a trusted partner who listens and leads with purpose. The right fractional fit creates real relationships with teams, delivers measurable results, and solves specific challenges with focus and intention.
Fractional Meaning Myths
Even when you know what fractional means, there’s often still some confusion. Let’s bust three of the most common:
Myth #1: Fractional Means Less Commitment
One common misconception about the meaning of fractional is that it’s just a temporary, detached relationship that’s only lightly involved with the team. In reality, fractional leaders are often brought in to own outcomes—not just observe them.
The difference isn’t just in the commitment to the team; it’s in the focus. Fractional executives focus on what really requires their senior-level expertise. That could be strategy, execution, decision making, leadership, or more. By staying focused and avoiding unnecessary administrative noise, they’re often able to deliver more impact in less time.
In other words, fractional doesn’t mean half or quarter in. It means fully invested, only with greater intention.
Myth #2: Fractional Is Just Another Word for Consultant
A lot of companies get tripped up here. Consultants typically advise from the outside. They analyze, recommend, and hand off the execution. Fractional leaders, on the other hand, step into the business to work hand in hand with your team. They’re available to help execute strategy and are held accountable for the results.
In short, fractional executives don’t just tell your team what to do. They help ensure it gets done. They attend leadership meetings, navigate real-world constraints, and adapt as the business evolves.
That type of embedded relationship is what takes it from simple advice to active leadership.
Myth #3: Fractional Is a Short-Term Fix
Many business leaders believe fractional leadership is only useful for short-term crises or transitions. And yes, fractional leadership can be incredibly effective during times like these. But it’s not the whole story.
Fractional executives can serve as a strategic bridge, helping the company thoughtfully scale, assess leadership needs, and bring in expertise as needed. They can also be used for years, as the fractional leadership delivers value without unnecessary overhead.
Rather than treating fractional hiring as a stopgap, consider it a smart, flexible way to enhance leadership capacity as your business grows and changes.
Meaningful Relationships: More Than a Transaction
One important yet overlooked part of the fractional meaning is the relationship itself. Fractional leaders are embedded into your team, so they learn how your business really works—the goals, constraints, culture, and responsibilities. This allows them to build trust over time rather than remaining at arm’s length.
The relationship-driven approach is what separates fractional leaders from short-term help or project-based support. A fractional executive becomes a true extension of your leadership team—someone your team can turn to for direction and clarity.
In addition, fractional leaders aren’t trying to climb internal ladders or get a better title, so the relationship tends to be more honest and productive. Conversations get real; decisions are clear; and teams have a steady, experienced presence without office hierarchy or politics getting in the way. Combined, this can lead to:
- Consistent collaboration between founders and senior leaders
- Clear communications across teams (breaking down silos)
- Leadership that listens as much as it guides
This facilitates greater trust, enabling more meaningful work to happen faster with less friction.
Meaningful Results: Experience That Scales
Relationships are important, but in business, what really matters is results.
Fractional executives come in to solve real issues with a clear mandate. Their experience helps shape ideas and strategies and then turns those into action. They’re able to cut through complexity, prioritize actions, and move initiatives forward.
In addition, because fractional leaders have been there before, they know what works—and what doesn’t. They can recognize patterns, avoid common missteps, and make more confident decisions. Ultimately, that can lead to faster progress, fewer costly detours, and a better use of time and resources.
Being a fractional leader also means they’re accountable for the results. They don’t just come up with some suggestions and walk away. They stay involved, adapt the plan to on-the-ground changes, and help ensure progress continues, resulting in measurable improvements in performance, process, impact, or profitability.
Meaningful Solutions Right When You Need Them
Fractional meaning isn’t about getting the right people on the bus or filling out an org chart. It’s about solving the right problems at the right times.
By providing senior-level expertise without a full-time commitment (and benefits package), companies have greater flexibility to respond to real needs as they arise. Scope, focus, and engagement can all adjust as the business changes, which can be especially powerful in a fast-moving environment.
Most importantly, these meaningful solutions don’t just address today’s issues—with clarity and structure, they help build a solid foundation for whatever comes next.
The Real Meaning of Factional
The true factional meaning is not about settling for part-time support. It’s a smarter, more intentional approach to promoting your company’s growth by building meaningful relationships, delivering meaningful results, and providing meaningful solutions.
If you’re exploring what comes next—whether that’s growth, transition, or simply a clearer direction—factional leadership may just be the most meaningful step forward. Start with a conversation with Next Fractional and discover how the right expertise—at the right time—can promote your business’s growth.




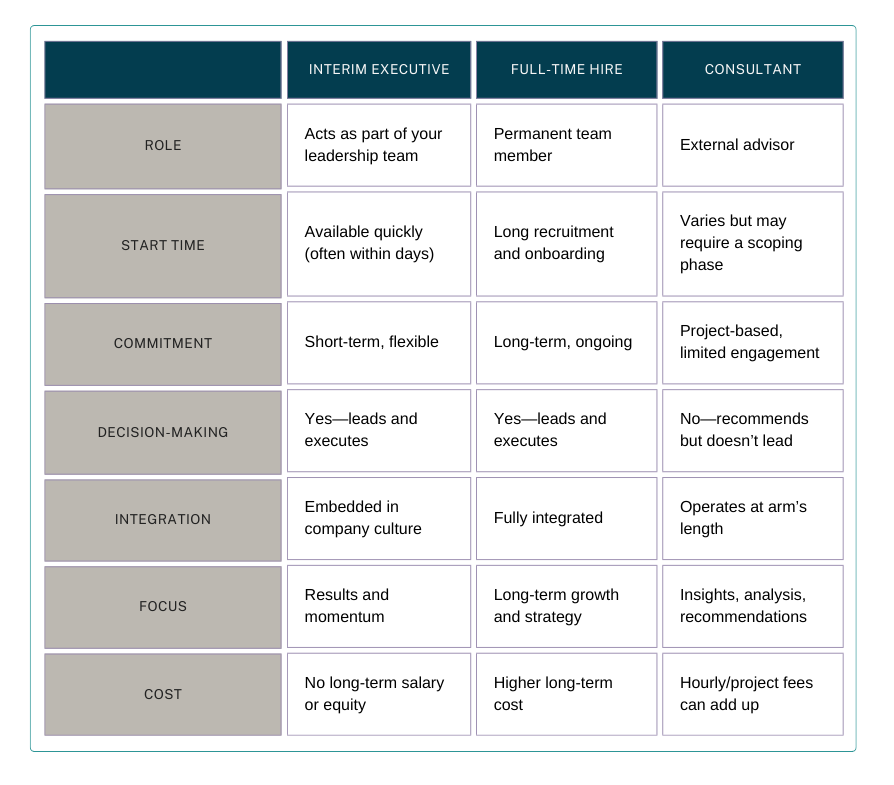 When Does Interim Management Make Sense?
When Does Interim Management Make Sense?
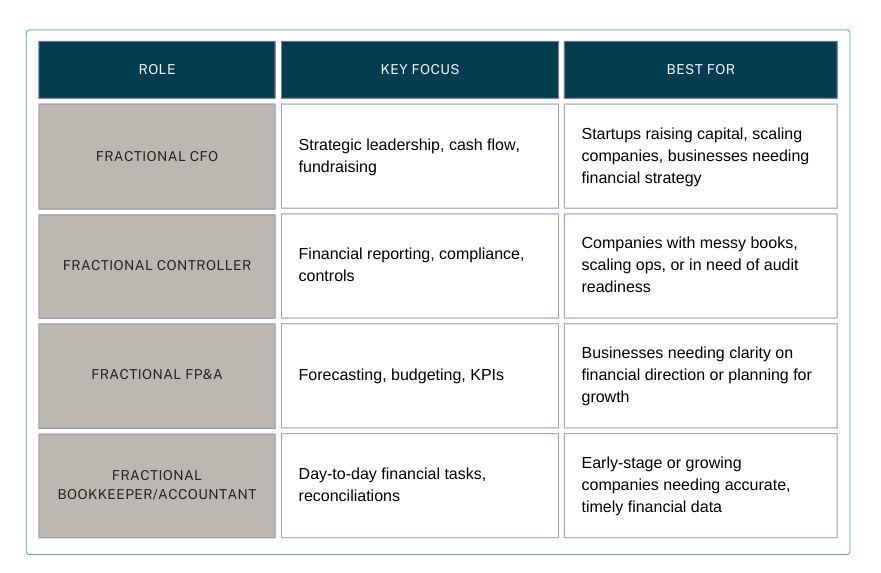 Benefits of Fractional Finance Management
Benefits of Fractional Finance Management
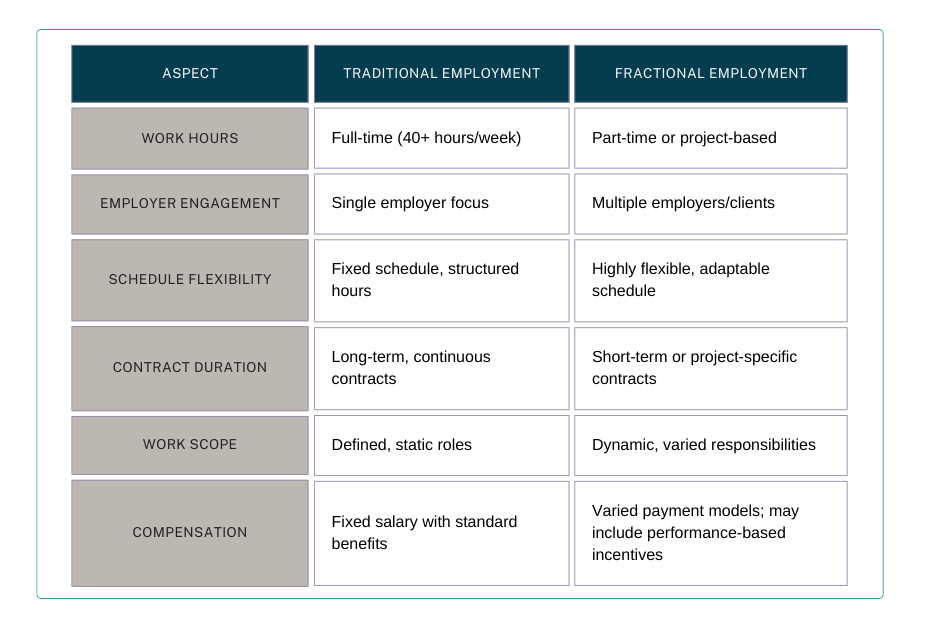 Anatomy of a Fractional Contract
Anatomy of a Fractional Contract